Apple Pay | Features, Updates, Availability
AppleInsider may earn an affiliate commission on purchases made through links on our site.
While it initially launched in 2013 only in the United States, Apple Pay is now available in over 50 countries and territories globally. Many major retailers accept it, and most major point-of-sale retail terminals can process tap-to-pay transactions.
Apple Pay saw a large surge in users in 2020 after contactless payments became popular as a health-related choice. Estimates place the payment system at around 500 million users as of December 2020.
According to one study performed by Pulse, Apple Pay transactions made up 92% of US mobile wallet debit transactions in 2020. This number indicates that despite Apple’s lower install base compared to Android, its payment system is dominating the mobile space.
Mục Lục
Apple Pay Features
The Apple Wallet is the app that stores Apple Pay cards and data. There is a dedicated Wallet app on iPhone and Apple Watch, and menus in Settings on iPad and Mac.
How Apple Pay works
By using an iPhone’s near field communications (NFC) chip, Apple Pay can wirelessly communicate with point-of-sale systems to initiate a contactless payment, or what is often referred to as “tap to pay” transactions.
Tap to pay transactions are often highly praised by both customers and retailers. Some suppliers have claimed that tap to pay transactions are up to twice as fast as traditional methods.
During a sale, a buyer will activate Apple Play via double-clicking the side button on Face ID enabled iPhones, or double-clicking the Home Button on Touch ID enabled iPhones. After they select which card to use, a buyer must hold their device near a point-of-sale terminal. The device will provide the necessary information, such as the device ID and a tokenized card number, to the terminal.
The buyer will need to authenticate the sale, usually either through Face ID or Touch ID. At no point is the buyer’s card information shared with the merchant, as the original card number is not stored on the device anyway.
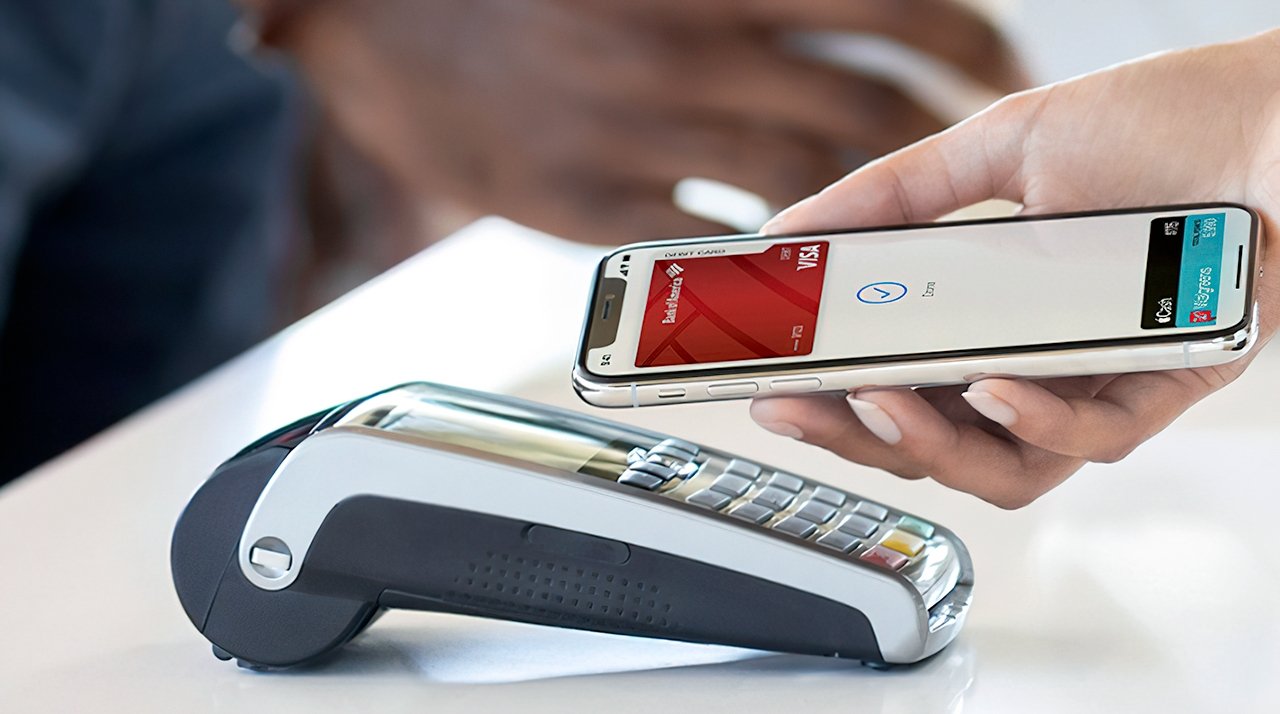

Apple Pay is much faster than traditional credit card swipes
Apple Pay uses an EMV-mode form of payment, similar to credit and debit cards that utilize integrated circuit chips. EMV is a technical standard that protects the buyer from security fraud by preventing cloning of the card by traditional methods that made cloning magnetic-stripe cards easy.
Adding cards to Apple Pay
A user can add eight cards on any device released before the iPhone 8, and twelve cards on the iPhone 8, iPhone 8 Plus, and later devices. A user will need to add each card to each device if they want to use Apple Pay on more than one device.
Once a card is authenticated on a device, new devices with the same account will only need a quick verification with the bank to add it to the new device.
Adding cards can be done by manually entering the information, scanning the card in via the device’s camera, or through the card issuers app if they allow it.
In certain countries, a user can add store cards, boarding passes, movie tickets, coupons, rewards cards, transit cards, and student ID cards to Wallet. The process for using these cards and services is similar to using a credit or debit card.
Transit cards and student ID cards will work on a device even if the battery is depleted to ensure owners can still access their services no matter what.
Apple Pay Later
Apple introduced a buy now, pay later service that is built into Apple Pay and Apple Wallet called Apple Pay Later. Customers can make purchases with a line of credit that must be paid back using a debit card in monthly installments.

Apple Pay Later is a buy now, pay later service in Apple Wallet
The system began rolling out to customers on March 28, 2023. The users’ credit will have a soft pull performed when making a purchase via Apple Pay Later to determine eligibility, so applying and being denied won’t affect credit scores.
Tap to Pay on iPhone
Apple announced Tap to Pay on iPhone in 2022 for third-party merchants. Payment processors no longer need to rely upon external registers or devices to accept payments. Instead, the customer can tap their iPhone to the merchant’s iPhone.
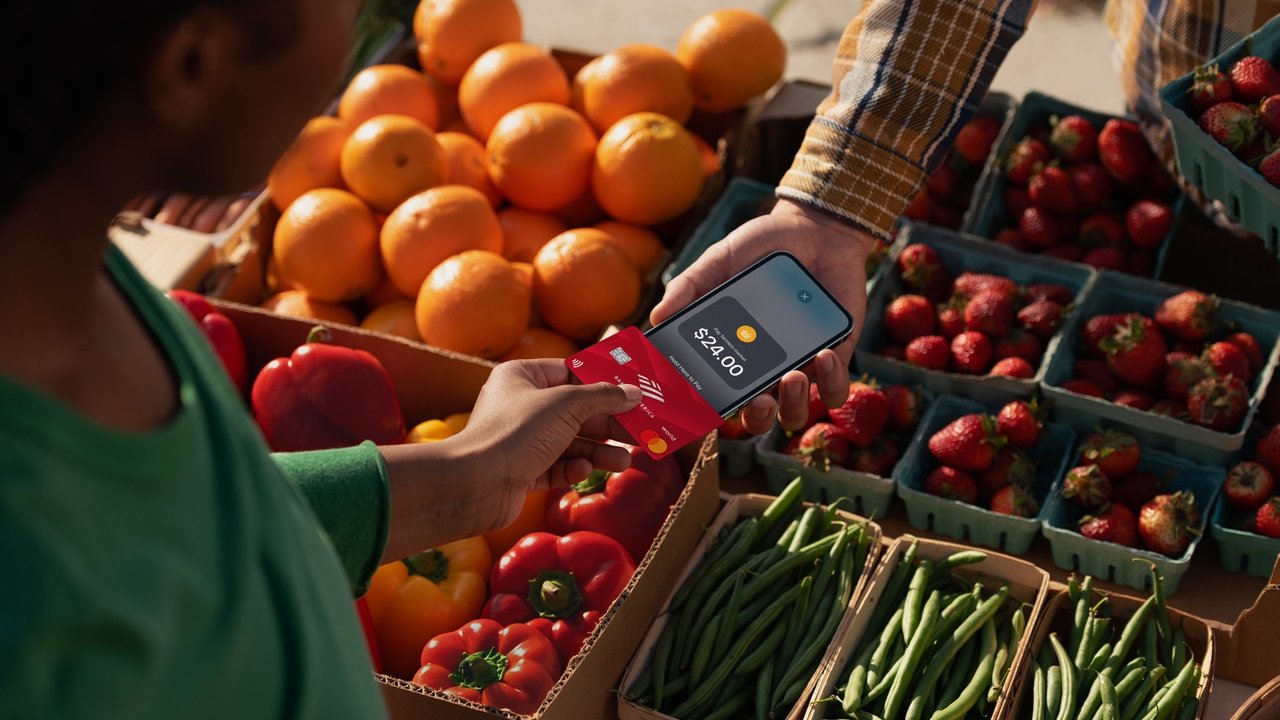

The iPhone will also accept cards with NFC tap chips
Cards that have contactless payment features will also work with the merchant’s iPhone. Users can simply tap their card on the iPhone to submit payment.
Third-party companies like Stripe and Paypal have integrated the feature. As always, privacy is at the center of this feature to prevent fraud or customer tracking by using encryption for all transactions
The Apple Card
In 2019, Apple, with the help of Goldman Sachs, launched the Apple Card. The Apple Card is designed primarily to be used with Apple Pay, though a physical card does exist. By visiting their Wallet app, a user can view their spending habits.
Using the Apple Card, either online or at a point-of-sale terminal will merit a user 2% cashback in the form of Apple Cash at most retailers. At certain retailers, including Apple, Uber, Walgreens, and Nike, users may earn 3% back when using the Apple Card.
Apple Pay Cash
Apple Pay Cash is a debit card operated via Green Dot bank. Customers can attach a bank account to the card to add cash or transfer it back to their originating bank.
 Apple Pay Cash has moved to Visa
Apple Pay Cash has moved to Visa
The balance on the card can be used anywhere a credit card is accepted. Apple Pay in the real world and on the web both support using Apple Pay Cash, so long as the card distributor is supported.
When Apple Pay Cash launched, it used a Discovery card number. In April 2022 Apple shifted new cards to a Visa number instead. Apple didn’t disclose the reason behind this shift, but the bank operator remained the same — Green Dot.
Apple Pay Cash also functions as a peer-to-peer payment system. Users can send money to other iMessage users in a text message. Parents can also set up Cash for their children’s accounts to distribute allowances.
When a user earns cashback from the Apple Card, it is deposited onto the Apple Cash card and can then be used for payments.
App Clips
Apple announced a new feature in iOS 14 that will take advantage of Apple Pay. App Clips are a new system for presenting pieces of an app to customers without requiring a full download.
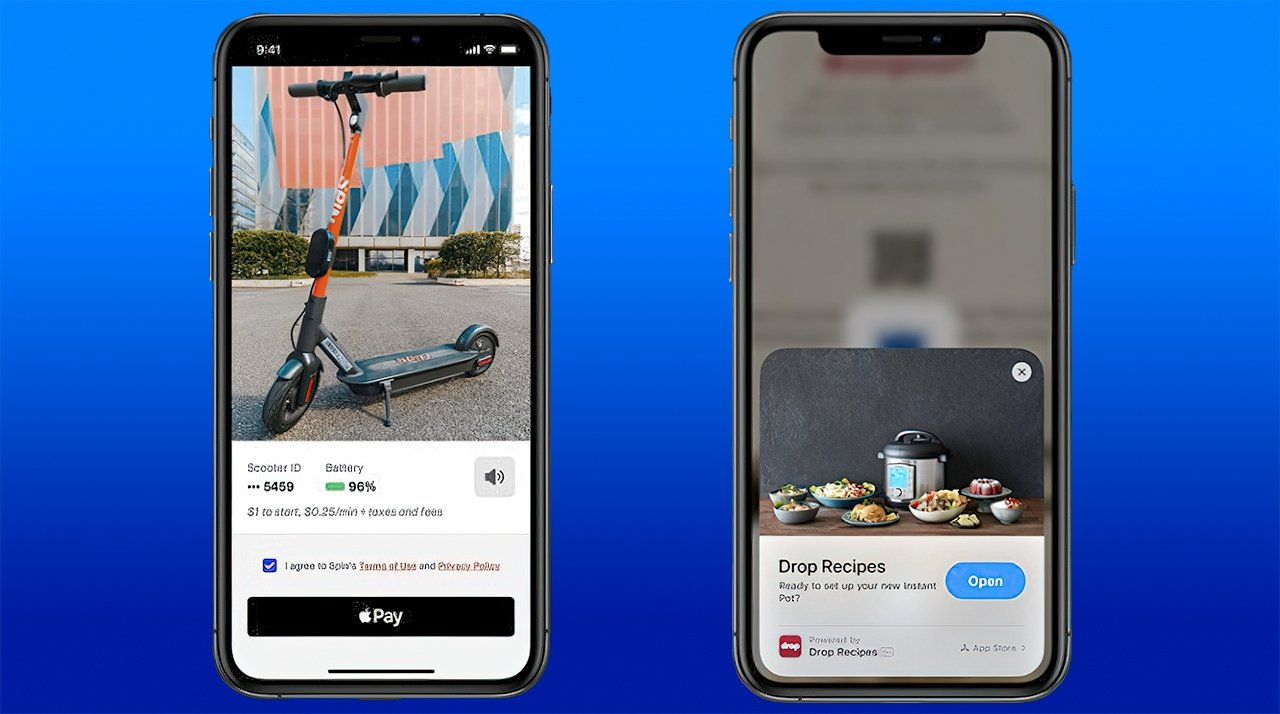
App Clips will let users interact with parts of an app without a full App Store download
Users will be presented with app clips while browsing their device, or when tapping an NFC sticker or scanning a specialized QR code. The App Clip shows up as a card on the screen where you will sign in with Apple and use Apple Pay to finish a transaction.
These App Clips are meant to streamline the entire process of one-time app interactions like with parking meters or scooters. Companies like Yelp can also build App Clips for specific restaurants or businesses so users are not directed back to the app when looking up information.
App Clips are designed to be very small, and Apple has placed a 10MB limit on developers. The App Clips you interact with are not saved to the device home screen, but can be found in a special folder in the App Library.
Compatible devices
The Apple Card heat map shows how often you spend in certain categories
Apple Pay is compatible with iPhone 6 and newer phones, the iPad Air 2 and more modern iPads, all Apple Watches, and any Mac that uses Touch ID.
If a user has an iPhone 5 or iPhone 5C, they can use it provided they also have an Apple Watch.
Also, when making purchases via Safari on a Mac, users can authenticate Apple Pay purchases using their nearby iPhone or Apple Watch.
Security benefits
Apple Pay adds a layer of security by obscuring personal data of the user from the retailer. Instead of offering the customer’s credit or debit card number, it replaces the number with a tokenized Device Primary Account Number.
Utilizing the DPAN, each transaction gets a unique dynamic security code. Apple does not track usage for third-party cards.
Each purchase also requires the use of a second-factor authentication method, either by Face ID, Touch ID, or passcode. When used on an Apple Watch, the watch must be unlocked and worn on the wrist to initiate payment, and the purchase must be authenticated by double-clicking the side button.
In the event that a user loses their device, it can be remotely suspended via the Find My feature.
Health Benefits
As strange as it may seem to consider, but Apple Pay does offer some health benefits to its users. Not a priority for discussion before, but the need for contactless payment systems is on the rise amid the coronavirus outbreak.
Markets are taking notice as users demand such contactless payments be accepted, since handing over money or cards all require some form of contact.
The implementation of such systems also requires some input from the store itself, as requiring a pin or zip code during a transaction with Apple Pay will still defeat the purpose of being contactless.
During the outbreak, one supermarket chain took the initiative to add Apple Pay, effective March 31, 2020, called Publix. This supermarket is distributed in the southern states of the US.
Controversy and criticism
Apple’s NFC chip, which enables contactless payment, can only be accessed via Apple Pay and Siri Shortcut automations. Restricting access prevents third-party apps, such as those used by credit card and bank card issuers, from being able to use it for their purposes.
Apple argues that limiting access to the NFC chip provides tighter security, citing that this is the reason that users choose Apple’s payment system in the first place.
Rival payment services have argued that this makes alternative payments less attractive and that it is evidence of anti-competitive and self-preferential practices.
In late 2018, Apple had settled a complaint with the Swiss payment company, TWINT, to avoid an antitrust probing. However, in mid-2019, the European Union began to question online retailers about their experience with Apple’s service.
Countries and regions where Apple Pay is accepted
Africa
- South Africa
Asia-Pacific
- Australia
- China mainland
- Hong Kong
- Japan
- Kazakhstan
- Macao
- New Zealand
- Singapore
- Taiwan
Europe
- Austria
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Faroe Islands
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Greenland
- Guernsey
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Isle of Man
- Italy
- Jersey
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Malta
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- Vatican City
Latin America and the Caribbean
- Brazil
- Mexico
Middle East
- Israel
- Saudi Arabia
- United Arab Emirates
North America
- Canada
- United States






