MySQL GROUP BY Count | How GROUP BY count works in MySQL

Mục Lục
Introduction to MySQL GROUP BY Count
MySQL GROUP BY Count is a MySQL query that is responsible to show the grouping of rows on the basis of column values along with the aggregate function Count. Basically, the GROUP BY clause forms a cluster of rows into a type of summary table rows using the table column value or any expression. We also implement the GROUP BY clause with MySQL aggregate functions for grouping the rows with some calculated value in the column. This may include MAX, MIN, COUNT, SUM, and AVG, where it is used with a SELECT statement that provides info about every group in the result set. Similarly, when we apply COUNT() function together with this GROUP BY clause then, it will show the number of counts for each specified grouped rows in the table query.
Syntax
The following syntax is the basic structure to query using GROUP BY Count clause in MySQL:
Start Your Free Data Science Course
Hadoop, Data Science, Statistics & others
Code:
SELECT Col_1, Col_2,…., Col_n, AggregateFunction(Col_i) FROM TableName
WHERE Cond_Expr GROUP BY Col_1, Col_2,…, Col_n;
Explanation: With the SELECT statement, the GROUP BY clause is an option to be used for providing a grouped result set according to a specified column value. The comma-separated lists: Col_1, Col_2,…, Col_n, denotes the column values to be fetched in the result set and one of them will be defined for aggregate function and GROUP BY clause to write the proper query. Here, the MySQL will evaluate the GROUP BY clause only after the SELECT, FROM, and WHERE clauses but should be placed before ORDER BY, HAVING, and LIMIT clauses.
How GROUP BY count works in MySQL?
The GROUP BY clause is essential when we want a collection of result set having rows with similar values arranged into subgroups type. It summarizes the rows by the column data specified in the query. In the output set, the MySQL GROUP BY clause returns a single row for every arranged group. This method helps to decrease the number of rows in the set of results provided by MySQL. Generally, with this GROUP BY clause, we add some aggregate functions that include COUNT, SUM, MIN, MAX, and AVG that gives information about the groups formed by using the GROUP BY query in the result rows.
In MySQL, the aggregate function is responsible to execute the calculation of a set table rows and outputs a value. Thus, the COUNT() function here is used with the MySQL GROUP BY clause to complete calculation and then it gives a distinct value for every subgroup formed. If you want to display the result set with unique values to occur with the GROUP BY Count clause, then we need to use the DISTINCT operator just after the SELECT clause in the query and before the column names specified. For example,
SELECT DISTINCT ColumnName FROM TableName;
Using the COUNT() function with the GROUP BY clause, then the query will produce the number of values as the count for each subgroup created based on the table column values or expressions.
Examples to Implement MySQL GROUP BY Count
Let us demonstrate some examples using the GROUP BY clause and COUNT() function in MySQL to show the working of GROUP BY Count:
Example #1: Using GROUP BY Count on a single column
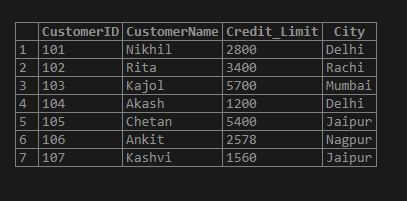
Step 1: Suppose, we have a Customer table in the database having the fields CustomerID, CustomerName, Credit_Limit, and City, where we have some records as follows:
Code:
SELECT * FROM Customer;
Output:
Step 2: Now, we will implement the MySQL GROUP BY COUNT to query the data forming groups based on the particular column value and each group has its own count number that is for the identical values found in the group. The SQL statement to perform this information in the result set rows with the following command.
Code:
SELECT CustomerName, City, COUNT(*) FROM Customer GROUP BY City;
Output:

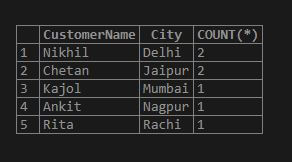
Explanation: You can see that the result rows are grouped by city column and each grouped value contains the count for that value present by which the rows are arranged. Thus, MySQL has returned a number of customers available in the table for each grouped city name. The group operation performed on the Customer table has displayed the reduced form of output rows due to the grouping of column values.
Example #2: Using GROUP BY Count on Multiple columns
Step 1: Let us take another table named Books present in our MySQL database. The table contains the fields as BookID, BookName, Language, and Price. To view the contents of the table we will execute the below query
Code:
SELECT * FROM Books;
Output:
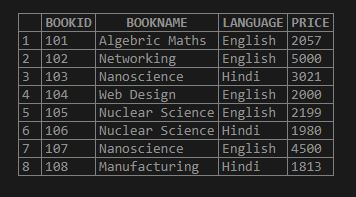
Step2: Here, we have a language column with values either ‘English’ or ‘Hindi’ and similarly we can find book names as per English medium and Hindi version too. Then, we will write a query to perform the grouping of columns in the table and also implementing the count function in it. The SQL statement is as follows:
Code:
SELECT BookName, Language, COUNT(*) FROM Books GROUP BY BookName, Language;
Output:
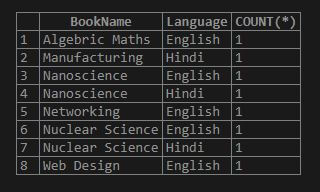
Explanation: As you can see the result rows are grouped based on multiple columns, BookName and Language using the GROUP BY operation and the next column is for the count that denotes values of books available for each group data in the table.
Example #3: Using GROUP BY Count with ORDER BY clause
For this illustration of an example, we will take the previous table named Books. In this query, along with the GROUP BY COUNT clause, we will also use the ORDER BY clause to evaluate the statement more properly. The ORDER BY clause in MySQL is responsible to arrange the column values irrespective of its data type either character or numeric, in ascending or descending order as mentioned in the query part. We will apply it after the GROUP BY clause. The query statement for this is as follows:
Code:
SELECT LANGUAGE, COUNT(*) FROM Books GROUP BY LANGUAGE ORDER BY 2 ASC;
Output:

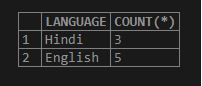
Explanation: Here, each group has its own respective counts and the counting for each group is queried in ascending order as shown above.
Conclusion
The COUNT() function in MySQL query will be used in conjunction with the clause GROUP BY which is useful to illustrate table records on the basis of several groupings. This GROUP BY COUNT query provides the count of values for the combination of identical column values that are preserved as a single group.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to MySQL GROUP BY Count. Here we discuss an introduction to MySQL GROUP BY Count, how does it work with query examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –






