iPhone 8 | Product timeline, specs, deals
AppleInsider may earn an affiliate commission on purchases made through links on our site.
Launched as part of Apple’s September 2017 event, the iPhone 8, and iPhone 8 Plus were considered the standard annual revision of the iPhone range. While the iPhone X boasted a new display and Face ID, the iPhone 8 device family gives users a more familiar design that retains the Home button, while also offering upgraded, higher-performance internals compared to 2016’s iPhone 7 range.
AppleInsider has reviewed both the iPhone 8 and iPhone 8 Plus, with both models scoring 4.0 out of a possible 5.
Mục Lục
External Design
Taking its cue from previous generations, the iPhone 8 and iPhone 8 Plus have the same general appearance of earlier devices. The iPhone 8 and iPhone 8 Plus have custom front and rear glass, made with a 50 percent deeper strengthening layer, fitted onto a steel substructure and surrounded with an aerospace-grade 7000 Series aluminum band.
At the top of the face side of both phones are the FaceTime camera, microphone, and speaker, with the Home button featuring Touch ID towards the base. At the bottom edge is a Lightning connector, another microphone, and a stereo speaker grille. On the left side are the volume buttons and the Ring/Silent switch, with a side button on the opposite edge.
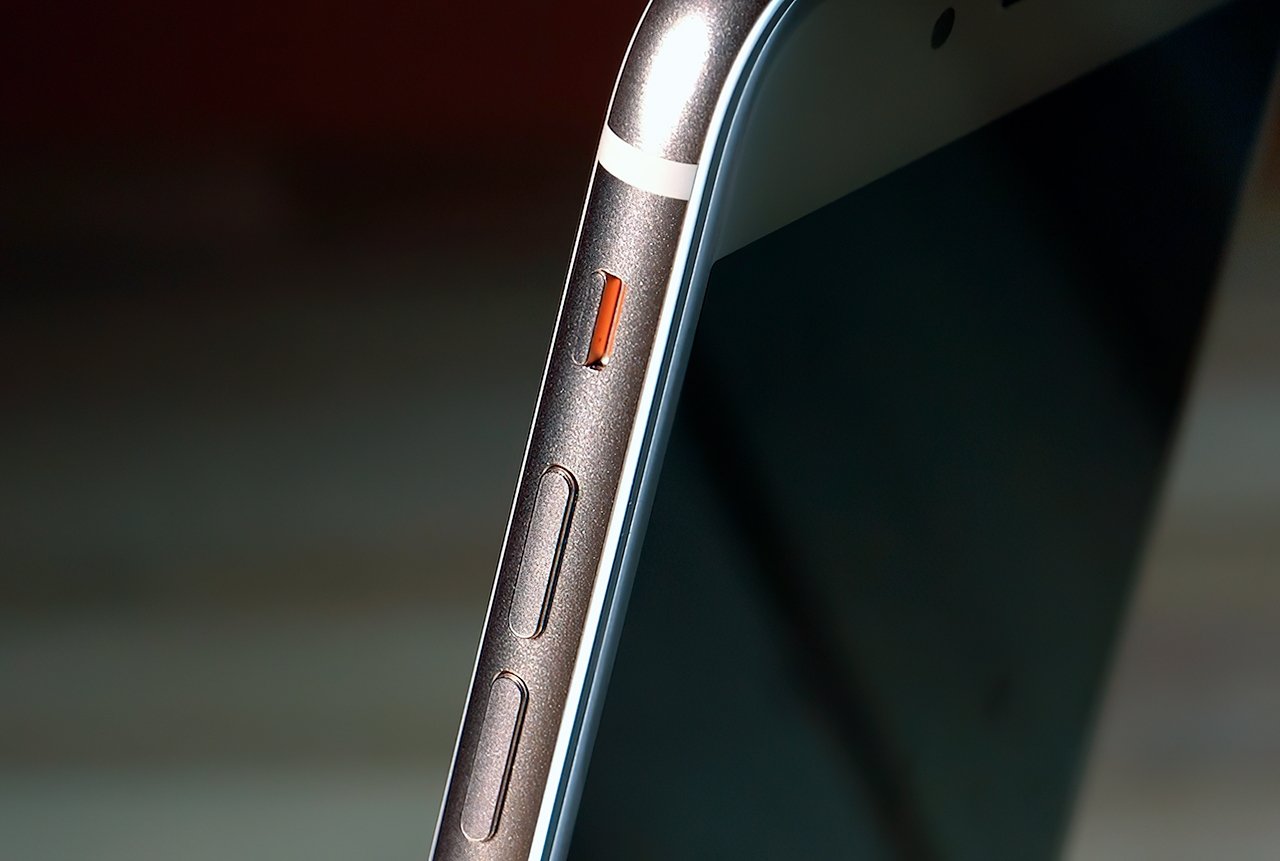

Apart from minor differences, this 2017 model continued with the design Apple had introduced with the iPhone 6
On the back side are the familiar camera bumps seen in previous generations. The standard model uses a single camera lens while the Plus variant has two camera sensors in the standard horizontal arrangement, with both sets of cameras flanked by a flash.
The smaller handset measures 5.45 inches tall by 2.65 inches wide and is 7.3 millimeters (0.29 inch) thick. The plus-sized model is much larger, measuring 6.24 inches tall by 3.07 inches wide, but is only 0.2 millimeters thicker at 7.7 millimeters (0.30 inch). While the iPhone 8 weighs 5.22 ounces, the bigger Plus weighs in at 7.13 ounces.
Continuing from the iPhone 7 family, both the iPhone 8 and iPhone 8 Plus have IP67 water and dust resistance.
Display
The iPhone 8’s display is a 4.7-inch LCD IPS screen, with a resolution of 1334 by 750 pixels, giving it a pixel density of 326ppi. The Plus has a 5.5-inch LCD IPS display, with its 1920 by 1080 resolution equating to a pixel density of 401ppi. In terms of contrast ratio, the iPhone 8’s is higher than the Plus, identified as 1400:1 and 1300:1 respectively.
The iPhone 8 has a 4.7-inch display
Both are Wide Color (P3) displays, offering a maximum brightness of 625 cd/m2, support 3D Touch, and have an oleophobic coating to minimize fingerprint marks.
New to the flagship iPhones that generation was True Tone, a display technology first seen in the 9.7-inch iPad Pro. Sensors monitoring the ambient light of the iPhone’s surroundings change the white point and brightness of the display to make it more comfortable to view in changing environments. It’s what Apple calls a “paper-like viewing experience.” TrueTone can also help ease eyestrain by changing the screen’s color, and prevent overexposure to blue-toned light.
A11 Bionic
The handset runs on the 64-bit A11 Bionic chip with M11 motion coprocessor, a chip that Apple also used for the iPhone X. The A11 improved on the A10 Fusion used in the iPhone 7 and iPhone 7 Plus by adding more cores, retaining the two high-power cores, and increasing the number of high-efficiency cores from the two to four.

The A11 Bionic powers Apple’s 2017 flagships
The chip offers better performance than the A10, with the high-efficiency cores claimed to be 70 percent faster in the A11, while the two performance cores offer a 25-percent improvement. It also includes the first Apple-designed GPU, 30 percent faster than the GPU used in the A10.
While the handset lacks the Face ID of the iPhone X, the A11’s power still made it more than capable of handling 3D applications and games, as well as the world-tracking and scene recognition requirements of augmented reality apps using ARKit.
Apple also included an updated image signal processor, which helped cameras to provide faster autofocus in low-light conditions, improved pixel processing, and better noise reduction.
Cameras
The phone has a single 12 megapixel f/1.8 camera on the back, equipped with a 5x digital zoom. The Plus model has two 12 megapixel cameras, with the wide-angle f/1.8 aperture camera accompanied by an f/2.8-aperture telephoto version. This pair of cameras offers an optical zoom and a 10x digital zoom.
Both versions use six-element lenses with a sapphire crystal lens cover and feature optical image stabilization, backside illumination sensors, a hybrid IR filter, and a quad-LED True Tone flash. Offering automatic image stabilization and HDR for photos, the rear cameras also include body and face detection, Live Photos with stabilization, autofocus using Focus Pixels, burst and timer modes, noise reduction, and improved local tone mapping.
For video, the rear cameras can capture 4K 60fps video, as well as 1080p at up to 120fps and 720p at 240 in slo-mo modes, with the latter two resolutions also able to use cinematic video stabilization alongside the optical image stabilization. Body and face detection is also available in video, as well as continuous autofocus, noise reduction, and the ability to take 8 megapixel still photos while recording 4K video. The Plus model is also able to use optical zoom in videos, as well as a 6x digital zoom.
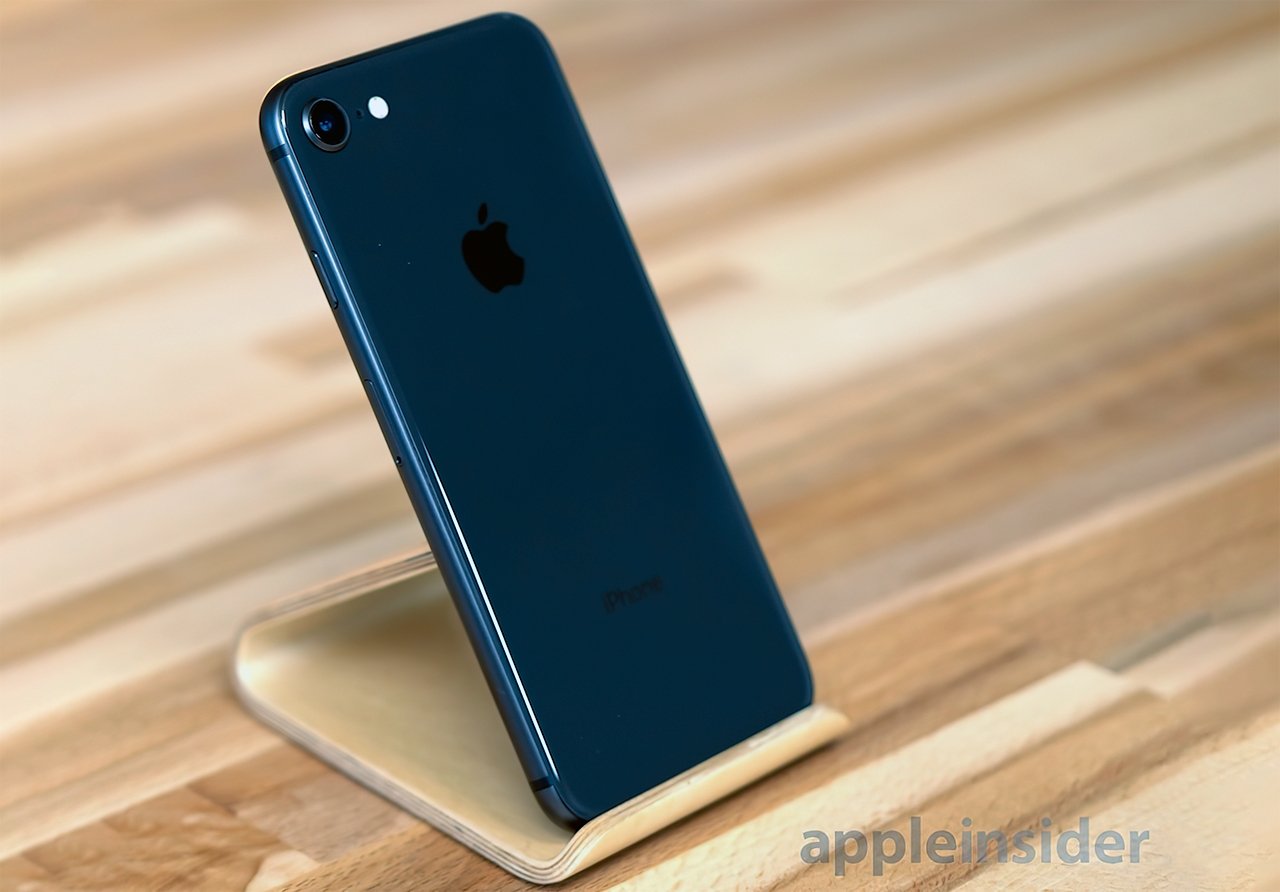

The phone has a single 12 megapixel f/1.8 camera on the back
On the front for both devices is the FaceTime HD camera, which uses a 7-megapixel BSI sensor and an aperture of ƒ/2.2. Capable of recording 1080p video, the FaceTime cameras offer automatic HDR for photographs, body and face detection, auto image stabilization, burst and timer modes, and a Retina Flash.
The plus-sized model also benefits from improvements to the Portrait mode, which uses the two rear cameras to produce a blurry bokeh effect in photographs. Portrait Lighting can apply five different lighting styles, changing not only the lighting effects visible on the subject but also potentially eliminating the background altogether. This can lend a stage lighting effect to the portrait.
To improve photographs in low-light situations, Apple has included a Slow-Sync flash feature that keeps the shutter open for longer and reduces the brightness of the flash itself. Though this can introduce motion blur, the resulting shot illuminates the subject evenly without any harsh bright spots, with more details visible in dark backgrounds.
Wireless Charging and Battery
According to Apple, the pair of 2017 phones lasts “about the same” as the iPhone 7 device family in terms of battery life.
The standard model is advised to have a talk time of up to 14 hours on a single charge, and lasts up to 12 hours for Internet use, up to 13 hours for wireless video playback, and up to 40 hours for wireless audio playback. The plus-sized model boosts the same usage types to maximums of 21 hours, 13 hours, 14 hours, and 60 hours respectively.
Both phones benefit from a fast-charge capability, which allows the smartphones to reach a 50 percent charge within 30 minutes. It is worth noting that this fast-charging performance won’t be available out of the box, as it will require Apple’s 29W USB-C power adaptors to attain that charging speed, instead of using the included 5W USB-A charger.
The glass back has enabled the iPhone to embrace wireless charging, with the iPhone 8 and iPhone 8 Plus supporting the open Qi protocol. This effectively allows the iPhone 8 to be charged using a wide array of existing wireless charging systems, including those installed in some stores and restaurants.
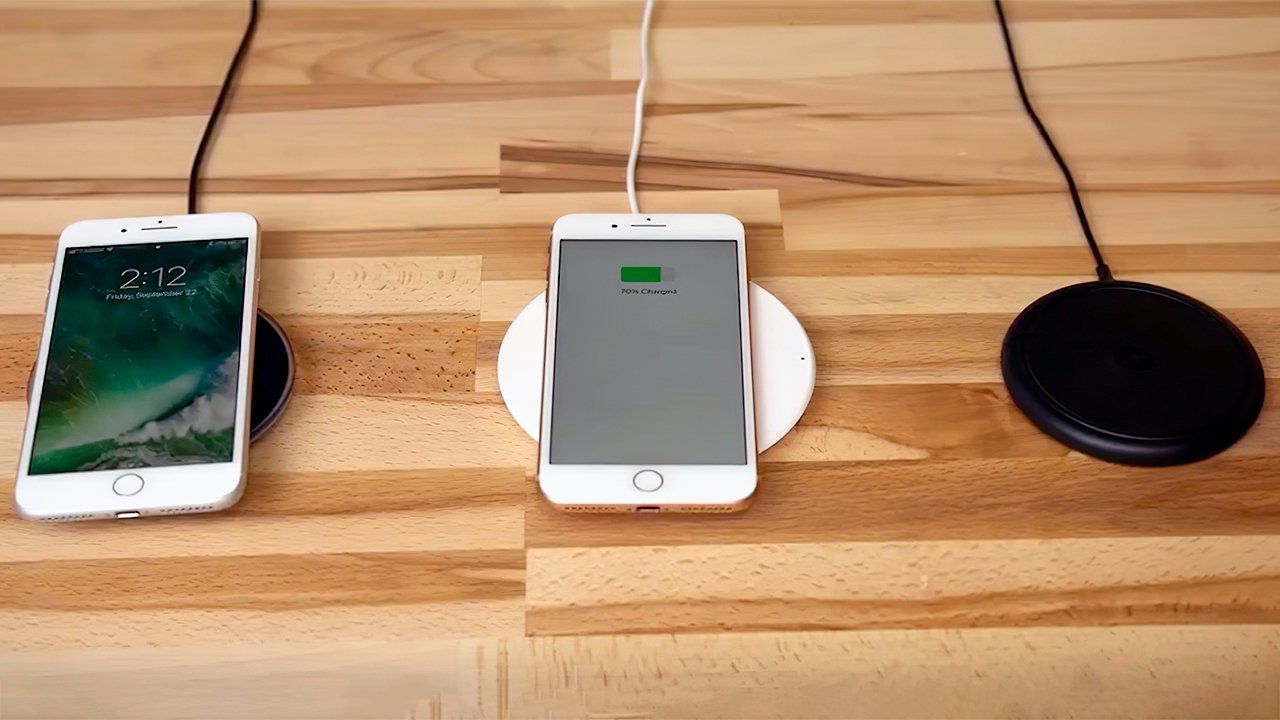

The phone lasts up to 14 hours for talk time and up to 12 hours for Internet use
AppleInsider’s testing of iPhone 8 charging methods revealed wireless charging occurs at roughly the same rate as a connection with the included 5W adapter, taking 2.5 hours to fully charge an iPhone 8 Plus.
Initially, the wireless charging capability was limited to 5 watts, but this has since changed. Included as part of the iOS 11.2 update, Apple has enabled all compatible wireless charging devices to transfer power at 7.5 watts, speeding up the battery recharge time when using the technology.
Using a combination of a 29W adapter and a USB-C to Lightning cable adapter that supports USB Power Delivery is the current fastest charging method at one and a half hours total, with the fast charging element allowing it to reach 52 percent charge after 30 minutes.
In October 2017, Apple issued a support document detailing the brands of auto maker that support iPhone wireless charging in their vehicles. The initial list included models from Buick, Cadilac, Chevrolet, and GMC, though it is noted that only specific models meeting the Qi standard Apple relies on will charge the iPhone.
Connectivity, Location, and Other Sensors
Apart from the Lightning port at the phone’s base, the wireless connectivity options in the handsets include 802.11ac Wi-Fi with MIMO, Bluetooth 5.0, and NFC connectivity, the latter of which can be used for Apple Pay transactions. Cellular connectivity ranges from GSM/EDGE to LTE, with Voice over LTE (VoLTE) supported by a number of carriers for higher quality call audio.
For navigation, supported satellite-based services include assisted GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and QZSS, with added support from cellular networks, Wi-Fi hotspots, and iBeacons. Other sensors, aside from the TrueDepth array, include a barometer, three-axis gyro, an accelerometer, proximity sensor, and ambient light sensor.
The phone includes a fingerprint reader incorporated into the Home button, used for Apple’s Touch ID authentication system. This was the last generation of flagship iPhones to include a Touch ID home button.
Colors, Pricing, and Availability
Both phones were sold in a choice of Silver, Gold, and Space Gray finishes. Pre-orders for both handsets commenced on September 15, 2017, and retail outlets and carriers started selling the smartphones from September 22.

The standard and plus-sized models from 2017
The smaller model shipped in two capacities, with the 64 gigabyte model priced at $699 full retail and the 256 gigabyte version for $849. The plus-sized model was also available in both capacities, priced at $799 and $949 off-contract, respectively.
Apple discontinued the two phones in April 2020 after the iPhone SE (second-generation) launch.
Reception
The new phone was in high demand when it went on sale, complete with lines outside some stores ahead of release. Apple CEO Tim Cook confirmed in a launch day interview that there were localized sellouts of the iPhone 8 and the Apple Watch Series 3, but advised there was still a “good supply” of devices heading to those locations.
There were some reports that there were low sales in some stores, including parts of New York City and Sydney. It is thought consumers waiting for the iPhone X may have contributed to the perceived reduced sales in these areas.
KGI analyst Ming-Chi Kuo played down reports of shorter lines, suggesting they were exaggerated by an “excessively negative market,” with a note to investors on September 16, 2017. Suggesting the iPhone 8 Plus outsold the iPhone 8, Kuo agreed that the lines were due to customers waiting for the iPhone X’s release but noted demand was still in line with Apple’s production plan.
The week before the iPhone X launch, a report from the Consumer Intelligence Research Partners claimed the 8-series family’s share of total iPhone sales in the United States looks similar to what an “iPhone 7s” would have been, based on previous sales data. The latest sales data also indicates the iPhone 8 Plus is outselling the iPhone 8.
Another report released at the same time by investment firm UBS and 451 Research polled 3,840 consumers about their buying intentions and reports the iPhone X and 8-series have generated more interest from consumers than in iPhone releases in the last two years.
The customary teardown from iFixit reports the iPhone 8 has a similar internal structure to the iPhone 7, with relatively few changes. Key alterations include the glass back and wireless charging, changes in screws used internally, a bracket to secure the Taptic Engine module, and new interconnects and cables for power and data routing.
A small number of iPhone 8 users reported issues with the smartphone’s audio in the opening days of availability, noticing a “crackling” or “static noise” from the ear speaker during calls. A statement from Apple on September 26 advised it was “aware of the issue,” and that a team was working on a fix “which will be included in an upcoming software release.”
Apple’s iOS 11.0.2 update, released on October 3, included a fix for the crackling problem.
Initial shipment estimates from Canalys suggest Apple has shipped approximately 11 million iPhones to China in the September quarter, a year-on-year increase of 40 percent, marking Apple’s best performance in the market in eight quarters. As well as overall increased sales, the mix of iPhone 8 sales at launch is also claimed to be higher than the corresponding mix of iPhone 7 sales at its own launch last year, despite high excitement for the iPhone X.
On November 11, 2017, supply chain reports from Kuo indicated the high sales of the iPhone 8 Plus was “cannibalizing demand” for the iPhone 8, prompting some of Apple’s manufacturing partners to switch production lines from the iPhone 8 to the Plus and the iPhone X to fix supply and demand balance issues.
The iOS 11.2 update on December 2 upgraded the wireless charging speed from 5 watts to 7.5 watts.
The iPhone 8 is compatible with iOS 16 in 2022, so some customers seek out this device as a cheap entry model.






