SQL SUM Function – Returns the Sum of Values
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the SQL SUM function to calculate the sum of all values or distinct values.
Mục Lục
Introduction to SQL SUM function
The SUM function returns the sum of numbers. The syntax of the SUM() function is as follows:
SUM( DISTINCT | ALL numeric_expression)
Unlike other SQL aggregate functions, the SUM() function accepts only the expression that evaluates to numerical values.
You can specify either ALL or DISTINCT modifier in the SUM() function.
- The
DISTINCTmodifier instructs theSUM()function to calculate the total of distinct values, which means the duplicates are eliminated. - The
ALLmodifier allows theSUM()function to return the sum of all values including duplicates. TheSUM()function uses theALLmodifier by default if you do not specify any modifier explicitly.
SQL SUM function examples
We will use the products table for our examples in the following sections.
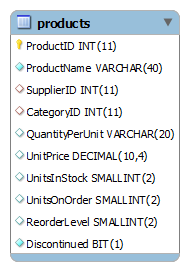
Simple SQL SUM function example
To get the sum of units in stock and the sum of units on order, you use the SUM() function as follows:
SELECT SUM(unitsinstock), SUM(unitsonOrder) FROM products;
SQL SUM with GROUP By clause example
To get the sum of units in stock by supplier, you use the SUM() function in conjunction with a GROUP BY clause as the following query:
SELECT supplierid, SUM(unitsinstock) FROM products GROUP BY supplierid;
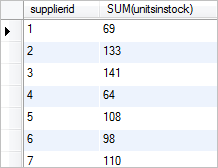
The GROUP BY clause groups the products by suppliers. For each group, the SUM() function calculate the sum of units in stock.
SQL SUM function with HAVING clause example
To get the sum of units in stock by supplier where the total units in stock is less than 50, you need to use the SUM() function with GROUP BY and HAVING clauses as shown below:
SELECT supplierid, SUM(unitsinstock) FROM products GROUP BY supplierid HAVING SUM(unitsinstock) < 50;
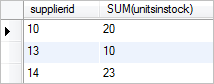
If you use a column alias for the expression that contains the SUM() function, you can refer to the alias in the HAVING clause instead of the expression. This helps you save time typing the same expression twice. In addition, when you change the expression, you have to change it in only one place.
The following query produces the same result as the query above.
SELECT supplierid, SUM(unitsinstock) totalinstock FROM products GROUP BY supplierid HAVING totalinstock < 50;

Advanced SQL SUM function examples
You can use the SUM function to answer more challenging business questions such as get top 5 customers by sales as the following query:
SELECT customers.customerid, companyname, (SUM(unitprice * quantity) - SUM(unitprice * quantity) * discount)AS
total FROM orderdetails INNER JOIN orders ON orders.orderid = orderdetails.orderid INNER JOIN customers ON customers.customerid = orders.customerid GROUP BY customers.customerid ORDER BY total DESC LIMIT5
Code language:
PHP
(
php
)
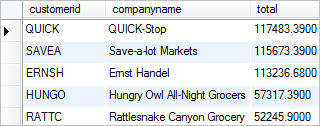
We use the LIMIT clause to get only 5 rows from the result set. Both MySQL and PostgreSQL support the LIMIT clause. In Microsoft SQL Server, you can use the SELECT TOP as shown in the following query to achieve the same result:
SELECT TOP5
customers.customerid, companyname, (SUM(unitprice * quantity) - SUM(unitprice * quantity) * discount)AS
total FROM orderdetails INNER JOIN orders ON orders.orderid = orderdetails.orderid INNER JOIN customers ON customers.customerid = orders.customerid GROUP BY customers.customerid ORDER BY total DESC;Code language:
PHP
(
php
)
The following query uses the SUM() function to get the 5 best selling products:
SELECT p.productid, p.productname, (SUM(o.unitprice * quantity) - SUM(o.unitprice * quantity) * discount) total FROM orderdetails o INNER JOIN products p ON p.productid = o.productid GROUP BY p.productid ORDER BY total DESC LIMIT 5;
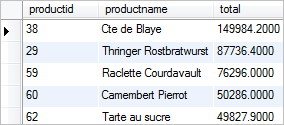
In this tutorial, we have shown you how to use the SQL SUM function to calculate the sum of values.






