Stone Age Art – Artlex

Stone Age art, also called prehistoric art, was created between the period of 40,000 BCE to 3000 BCE ending with the Bronze Age. Global prehistory is a period called lithic or stone ages. Prehistoric art from the Stone Ages is divided into three segments: Paleolithic or Old Stone Age art, 40,000 BCE to 10,000 BCE; Mesolithic Period or Middle Stone Age art, 10,000 BCE to 8,000 BCE; and the Neolithic Period or New Stone Age art from 8,000 BCE until 3,000 BCE.
Mục Lục
Famous Stone Age Art





What Were the Main Characteristics of Stone Age Art?
Two-dimensional and three-dimensional work from the Stone Age is collectively referred to as rock art. Types of works from this period include two-dimensional petroglyphs (engravings) and pictographs ( paintings), with human, animal, or geometric designs. Three-dimensional works such as sculptures were always prevalent in prehistoric art. The female figure was a particular focus in a form of work known as Venus art. There were also outdoor megaliths.
The Stone Age was a time a great climate shifts and environmental change in which the people had to adapt. Stone Age artists had to use what was available within this environment.
Materials used for drawing and painting include charcoal, clay ochre and manganese. For sculpture common materials Stone Age artists used included sandstone, limestone, quartzite, and steatite. Animal bones were used, as well as reindeer antlers. Ivory from mammoths was also utilized.
Prehistoric art was created before the written word so there is no record as to its purpose. Art historians and scientists have had to develop theories based on the art and architecture left behind. Each period of prehistoric art brought new and more advanced art as societies evolved. All are part of Stone Age art history.
Old Stone Age/Paleolithic Period – 40,000 BCE–10,000 BCE
Historians believe the first Old Stone Age communities were established in West, Central and East Asian between 70,000 and 40, 000 BCE. Given the vast time span the Old Stone Age or Paleolithic Period be further divided into Lower Paleolithic, Middle Paleolithic and Upper Paleolithic periods.
This was a nomadic stage in global prehistory when the people lived in huts and tepees.
The main concern was hunting and gathering. To accomplish this, the first crudely made stone tool and bone tools emerged. The people hunted for bison, deer, and mammoth, while also fishing. Berries, nuts, and fruits were gathered from the land.
The last Ice Age appeared at the end of the Paleolithic Period. The result caused an extinction of many animals, rising sea levels, climate change and a migration of the people.
Old Stone Age Cave Art
Paleolithic cave art were some of the very first creative arts in global prehistory. The works involved cave painting or etching. These cave painting and etchings give great insight into the history of the Stone Ages.
The white calcite Lascaux Cave in Lascaux, France is famous for human figural and animal paintings. These are fine examples of prehistoric cave art dating back to 15,000-13,000 BCE. The various passageways within the cave provide a gallery of over 2000 images.
The Great Hall of Bulls contains a large work just over 11 feet in length. Charcoal and ochre drawings consist of birds, bison, elk, deer, horses, and people appear on the cave walls. Pigments colors used include brown, black, red, yellow, and violet, which were obtained from local minerals. Hollowed bones found in the cave indicate that the paint was blown on to the wall.
Some art historians believe the cave paintings in Great Hall of Bulls is a narrative depicting a successful hunt. Others believe Stone Age painters used it to honors the animals in a bid to ensure future hunts will be successful.
This UNESCO World Heritage sites saw a large influx of visitors between 1940-1963. As a result, the site had to be closed to be preserved. Lascaux II is an exact replica located 200 meters away that visitors can now access.
Apollo 11 Stones, a work using charcoal and dating back to 25,500- 25,300 BCE was discovered in a cave in Namibia, Africa, in 1969. This was the same year as the Apollo 11 landed on the moon. The work depicts an animal, that art historians believe is a therianthrope, a creature in mythology that can shift shape. The work shows in twisted perspective and has anthropomorphic qualities. This stone is one of several found at the site.
Paleolithic Period Sculpture
Small portable sculptures were also made depicting people and animals. Fertility was a main theme as Venus art or small sculptures of women were crafted with enlarged sex organs, hips, and thighs
Archeologists from the Department of Prehistory at the German University of Tubingen discovered the oldest Venice figurine the Venus of Hohles Fels, also known as the Venus of Schelklingen dating to 38,000- 33,000 BCE. It was found in 2008, while excavating Hohles Fels Cave in the Swabian Jura of southwestern Germany. The Paleolithic art was carved out of a mammoth ivory tusk stands 2.4 inches tall and historians believe it was worn as an amulet.
The ivory carved Vogelherd Mammoth was found in intact in Hohlenstein mountain region in 2006. The sculpture dating back to 33,000 BCE is the first mammoth carving ever found. Both works are part of the university’s collection.
Mesolithic Period/Middle Stone Age – 10,000 BCE–8,000 BCE
Communities began to form during the Middle Stone Age. Although these were mostly still nomadic there were signs of some agriculture. Stone tools became more advanced with spears made from antlers and tips of objects sharpened into points. The use of fire encouraged the finishing of more sophisticated clay sculptures.
Mesolithic Cave Art
Human figures and life were the main subject matter of painting and engravings.
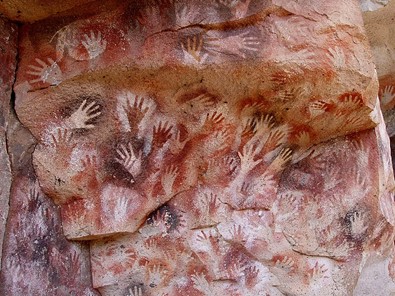
Cave paintings using human hands as stencils, along with abstract symbols were found at La Cueva de las Manos or Cave of Hands, in the Patagonia region of Argentina, dating back to 7300 BCE. The paint was mouth blown over the hand using hollowed out bones as straws.
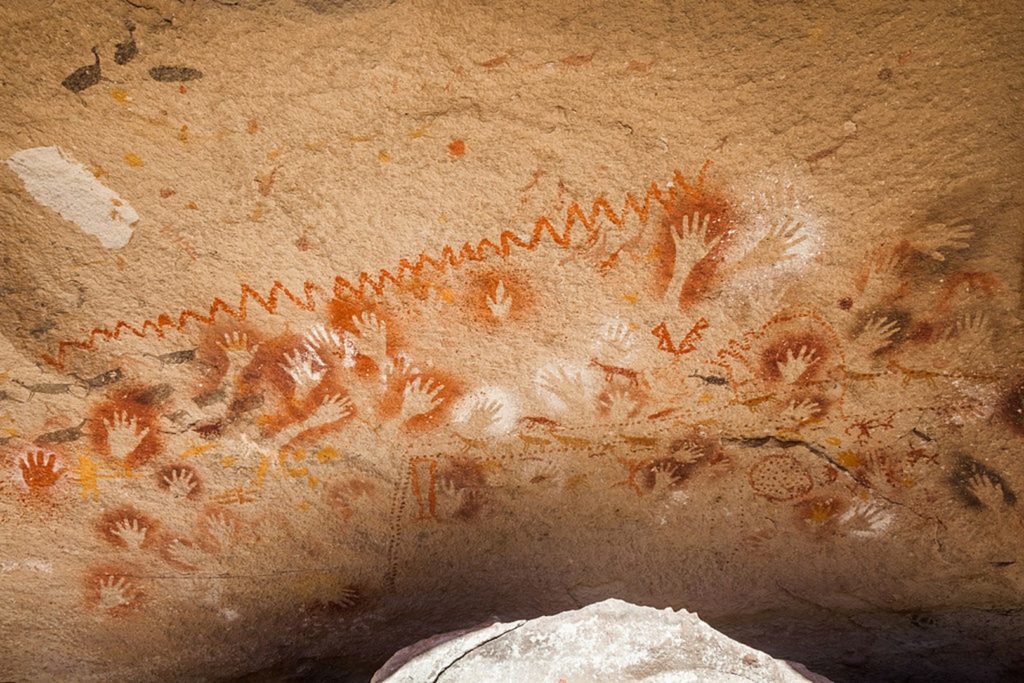

Over 200 hand stencils were created. Various pigments were used from nature including iron oxide to create red and purple and manganese oxide to create black. White pigment was made from kaolin and natrojarasite for yellow.
Also at La Cueva de las Manos over 150 petroglyphs were found of animals including horses, bison, ibexes, and mammoths appear on the cave walls.
Mesolithic Sculpture
Artists during the Mesolithic period favored relief sculptures. A smaller number of small stone sculptures were found. Trees were plentiful after the Ice Age and sculpture were also carved from wood.
Ceramic Art
Japanese Ceramic art from the Jomon culture of the 11th millennium BCE is most notable for the decorative patterned elements impressed into wet clay using sticks. Chinese pottery was embossed with stamps.
What is Megalithic Art?
Megalithic art was first developed during the Mesolithic period and hit its peak during the Neolithic period. It was created with large heavy stones that signified a sense of permanence.
In rock art terms one stone is called a menhir. This was often carved with patterns or pictures. Grouped together they form an assemblage. Stones were also used to build architectural spaces.
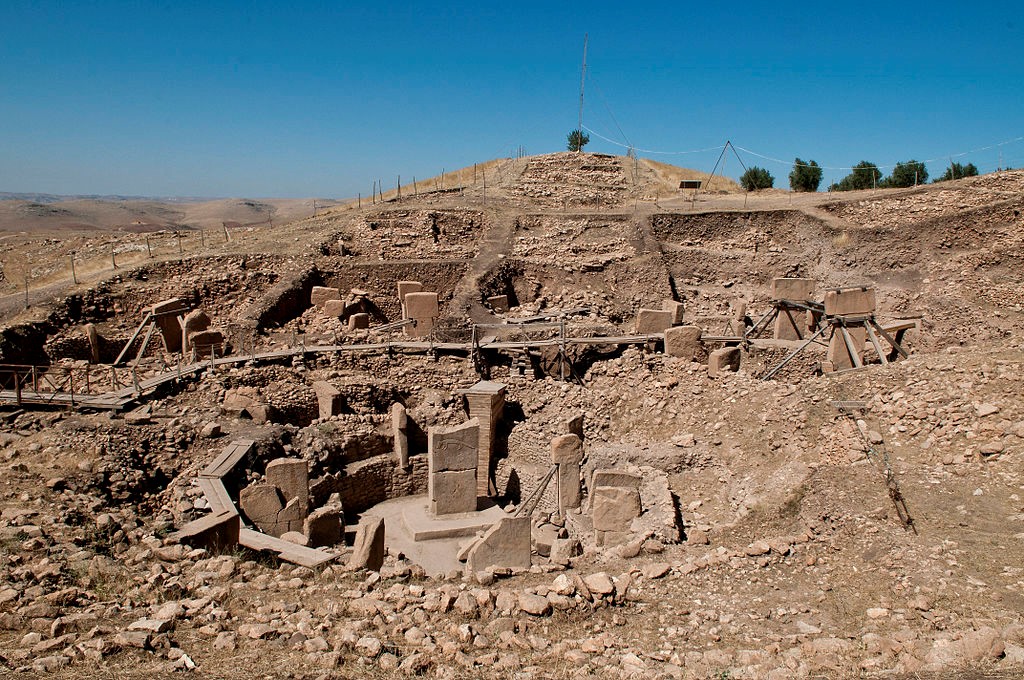
Gobeki Tepe (9500-7500 BCE) a monumental complex in Sanliurfa, in Southeastern Turkey, used megaliths to design shrines. The surrounding contains numerous reliefs of local animals.
Neolithic Period/New Stone Age – 8,000 BCE–3,000 BCE
The nomadic lifestyle ended and was replaced with agrarian communities. Societies were more sophisticated. Cereal grains were cultivated. Tools were constructed for plowing and tilling. Animals became domesticated.
During this time the first homes were constructed. Utilitarian objects were painted. Weaving of cloth fabrics was more developed as craftmanship of art progressed. People adorned themselves with jewelry.
Cities began to grow, while laws were implemented, and religion was practiced.
During the Neolithic period congs began to appear in the Jiangsu province of China, as part of the Liangzhu culture. The long tube with a wide whole in the center often has carvings on the side.
Only the elite could afford works in jade. Although found in tombs, art historians are still not sure what the purpose of the cong was.
The Building of Stonehenge
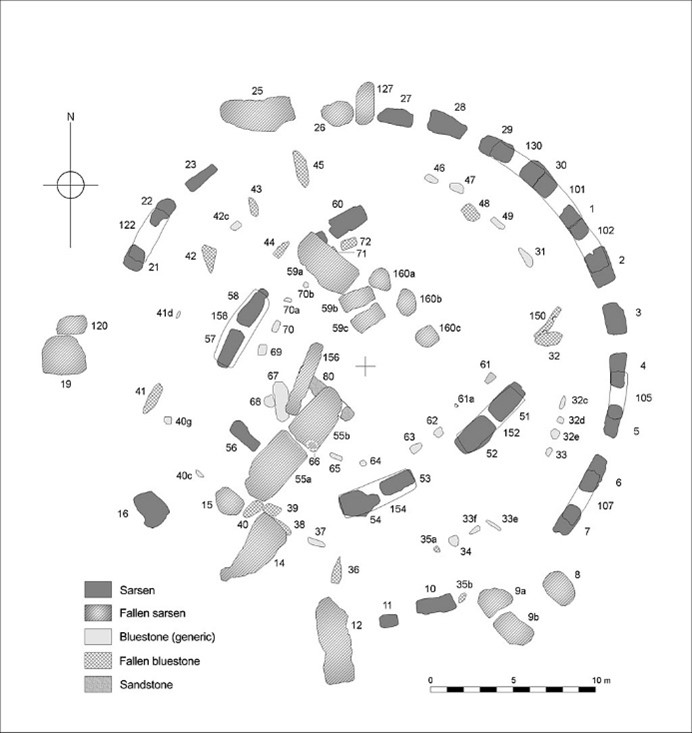
Stonehenge is a sandstone prehistoric European assemblage that was constructed between 3,000- 1,600 BCE. It stands alone on a large plain in Wiltshire, England, in the United Kingdom. The stones, measuring 30 feet tall were assembled in in a circular formation, the diameter of which measures 320 feet. While the sandstone is local, the inner blue stones are from Wales, over 200 miles away.
Human remains and bones found here indicate Stonehenge was once was once a burial ground. Tools found on the site show the construction was the work of many tribes over the years.
Large stones assembled and grouped together in a circular formation are referred to as a cromlech or henge.
Megaliths As Architectures During the Neolithic Period
Portal tombs or dolmen tombs were constructed using upright support stones with a capped roof, often covered with earth. Passage tombs were a further development made by adding long passages to the portals. A gallery grave is an elongated rectangle without a passage.
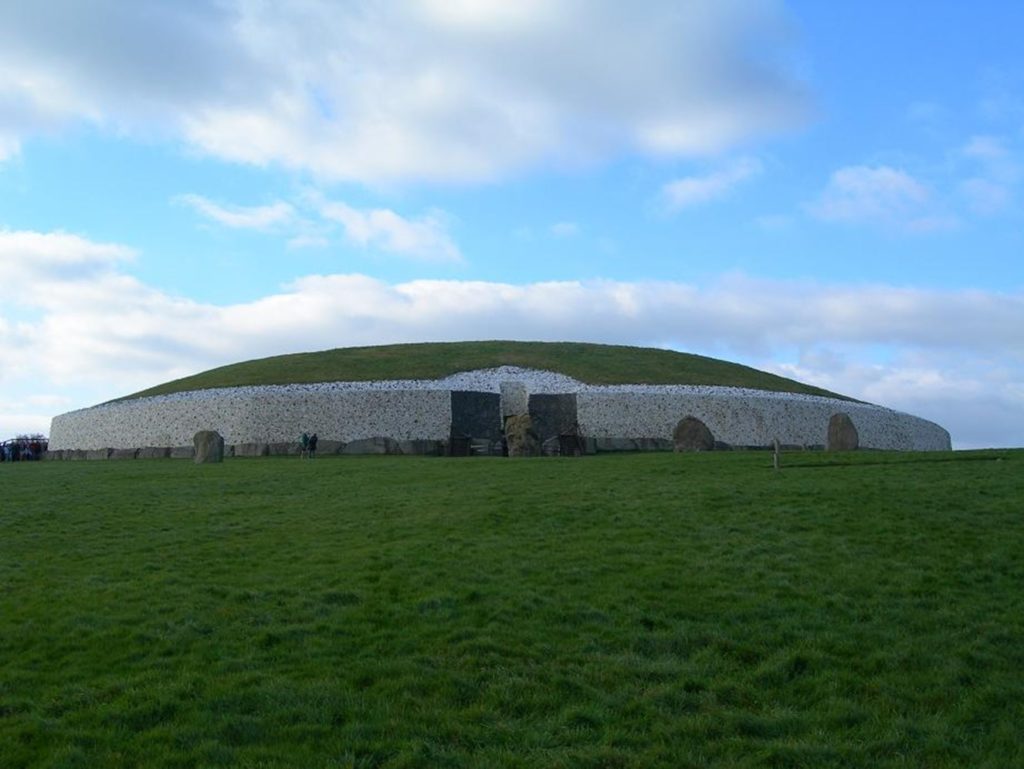
The monuments at Brú na Bóinne Complex, 50 km north of Dublin, in County Meath, Ireland had many functions. They were used for social, economic, and religious purposes.

There are three main passage tombs here as well as the largest concentration of megalithic art in all of Europe. Newgrange (3300-2900 BCE) was designed with a passage chamber that illuminates during the winter solstice. At its mouth is The Spiral of Life or Triple Spiral engraving, a menhir from 3100 BCE.
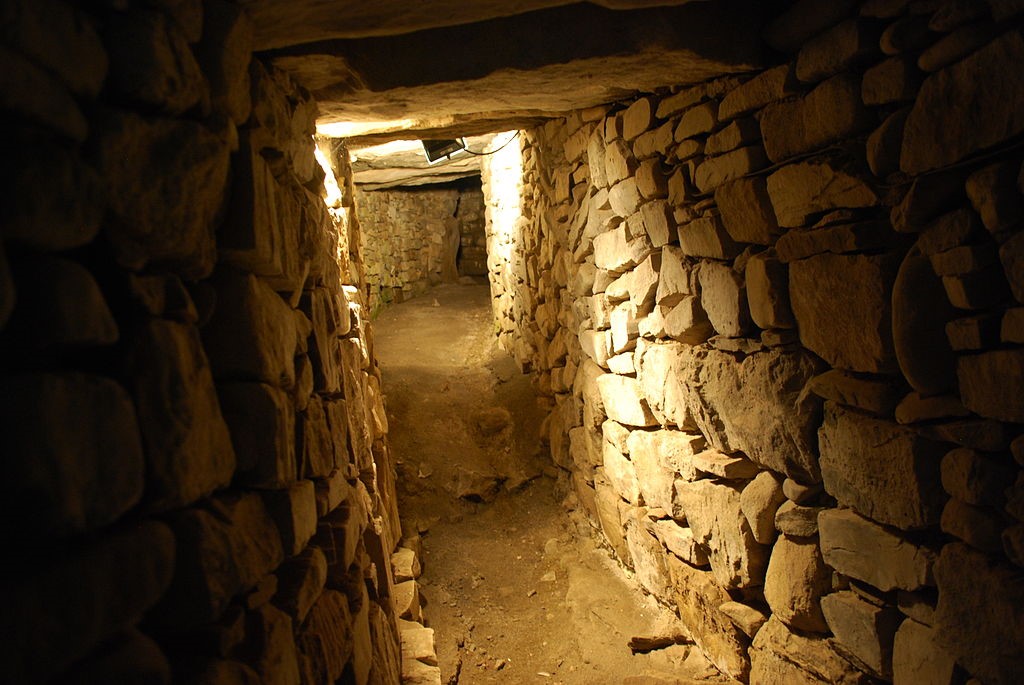

Knowth (3200 BCE) has two passageways. It is also surrounded by 17 satellite mounds. A multitude of rock art was found here with engravings with geometric patterns including spirals, crescents, and wave. Art historians are still puzzled by much of the symbolism.
Dowth (3200-2900 BCE) is situated about two miles away and suffered damage during an excavation in 1847.
The End of the Stone Age
The Stone Age ended in 3000 BCE with the dawn of the Bronze Age.
Stone Age Art Terms
- Anthropomorphic
- Cong
- Cromlech
- Henge
- Figurative: clearly derived from real objects or sources
- Stylized
- Twisted perspective/Composite view
- Thrianthrope
- Megalith / Monolith
- Menhir
- Cromlech
- Henge
- Portal tomb
- Dolmen
- Passage Tomb
- Gallery Grave






